Profile

|
Publications
DINO in the Room: Leveraging 2D Foundation Models for 3D Segmentation

Vision foundation models (VFMs) trained on large-scale image datasets provide high-quality features that have significantly advanced 2D visual recognition. However, their potential in 3D scene segmentation remains largely untapped, despite the common availability of 2D images alongside 3D point cloud datasets. While significant research has been dedicated to 2D-3D fusion, recent state-of-the-art 3D methods predominantly focus on 3D data, leaving the integration of VFMs into 3D models underexplored. In this work, we challenge this trend by introducing DITR, a generally applicable approach that extracts 2D foundation model features, projects them to 3D, and finally injects them into a 3D point cloud segmentation model. DITR achieves state-of-the-art results on both indoor and outdoor 3D semantic segmentation benchmarks. To enable the use of VFMs even when images are unavailable during inference, we additionally propose to pretrain 3D models by distilling 2D foundation models. By initializing the 3D backbone with knowledge distilled from 2D VFMs, we create a strong basis for downstream 3D segmentation tasks, ultimately boosting performance across various datasets.
@InProceedings{knaebel2025ditr,
title = {{DINO} in the Room: Leveraging {2D} Foundation Models for {3D} Segmentation},
author = {Knaebel, Karim and Yilmaz, Kadir and de Geus, Daan and Hermans, Alexander and Adrian, David and Linder, Timm and Leibe, Bastian},
booktitle = {2026 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV)},
year = {2026}
}
DONUT: A Decoder-Only Model for Trajectory Prediction
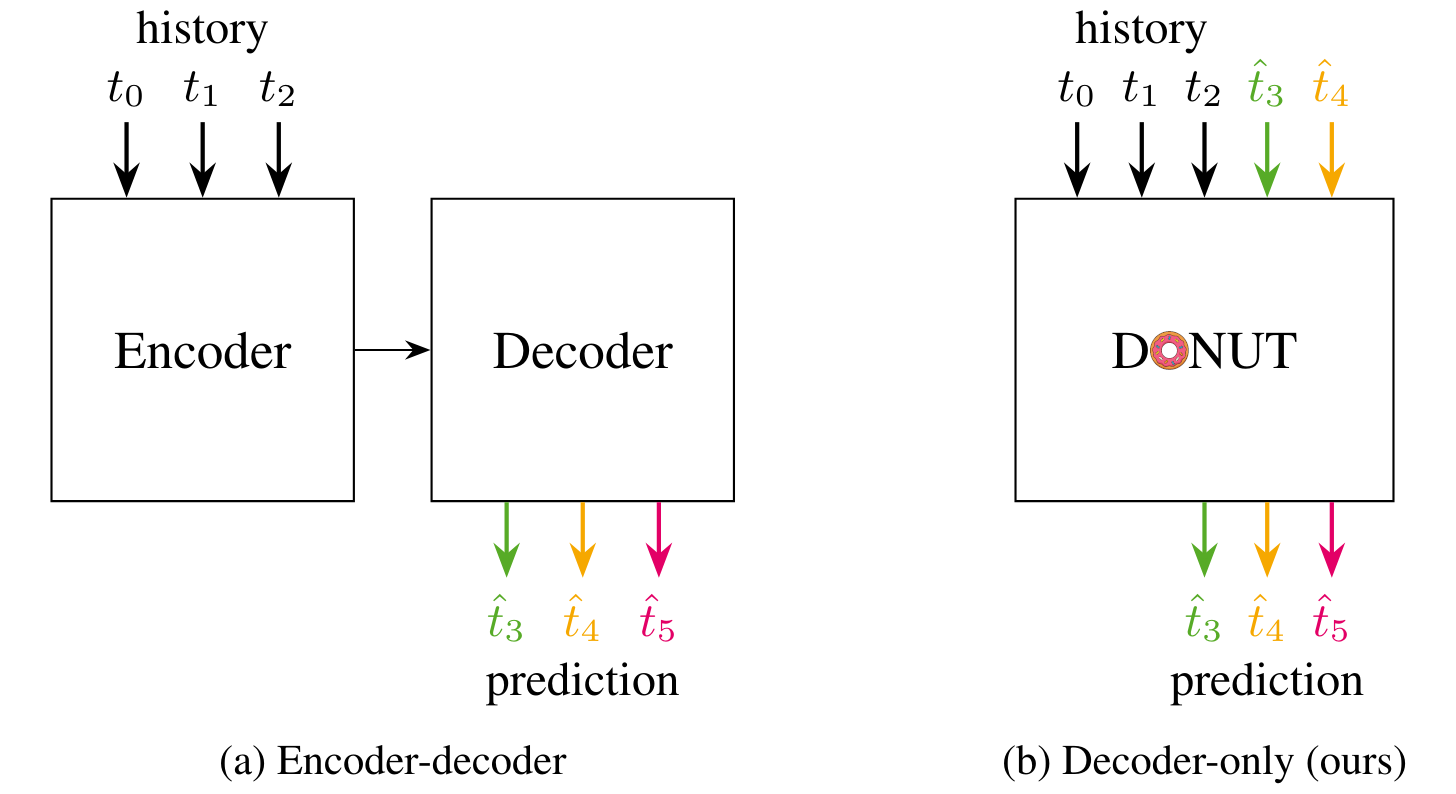
Predicting the motion of other agents in a scene is highly relevant for autonomous driving, as it allows a self-driving car to anticipate. Inspired by the success of decoder-only models for language modeling, we propose DONUT, a Decoder-Only Network for Unrolling Trajectories. Different from existing encoder-decoder forecasting models, we encode historical trajectories and predict future trajectories with a single autoregressive model. This allows the model to make iterative predictions in a consistent manner, and ensures that the model is always provided with up-to-date information, enhancing the performance. Furthermore, inspired by multi-token prediction for language modeling, we introduce an 'overprediction' strategy that gives the network the auxiliary task of predicting trajectories at longer temporal horizons. This allows the model to better anticipate the future, and further improves the performance. With experiments, we demonstrate that our decoder-only approach outperforms the encoder-decoder baseline, and achieves new state-of-the-art results on the Argoverse 2 single-agent motion forecasting benchmark.
@article{knoche2025donut,
title = {{DONUT: A Decoder-Only Model for Trajectory Prediction}},
author = {Knoche, Markus and de Geus, Daan and Leibe, Bastian},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2506.06854},
year = {2025}
}
Your ViT is Secretly an Image Segmentation Model

Vision Transformers (ViTs) have shown remarkable performance and scalability across various computer vision tasks. To apply single-scale ViTs to image segmentation, existing methods adopt a convolutional adapter to generate multi-scale features, a pixel decoder to fuse these features, and a Transformer decoder that uses the fused features to make predictions. In this paper, we show that the inductive biases introduced by these task-specific components can instead be learned by the ViT itself, given sufficiently large models and extensive pre-training. Based on these findings, we introduce the Encoder-only Mask Transformer (EoMT), which repurposes the plain ViT architecture to conduct image segmentation. With large-scale models and pre-training, EoMT obtains a segmentation accuracy similar to state-of-the-art models that use task-specific components. At the same time, EoMT is significantly faster than these methods due to its architectural simplicity, e.g., up to 4× faster with ViT-L. Across a range of model sizes, EoMT demonstrates an optimal balance between segmentation accuracy and prediction speed, suggesting that compute resources are better spent on scaling the ViT itself rather than adding architectural complexity. Code: https://www.tue-mps.org/eomt/.
@inproceedings{kerssies2025eomt,
author = {Kerssies, Tommie and Cavagnero, Niccol\`{o} and Hermans, Alexander and Norouzi, Narges and Averta, Giuseppe and Leibe, Bastian and Dubbelman, Gijs and {de Geus}, Daan},
title = {{Your ViT is Secretly an Image Segmentation Model}},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
year = {2025},
}
Fine-Tuning Image-Conditional Diffusion Models is Easier than You Think
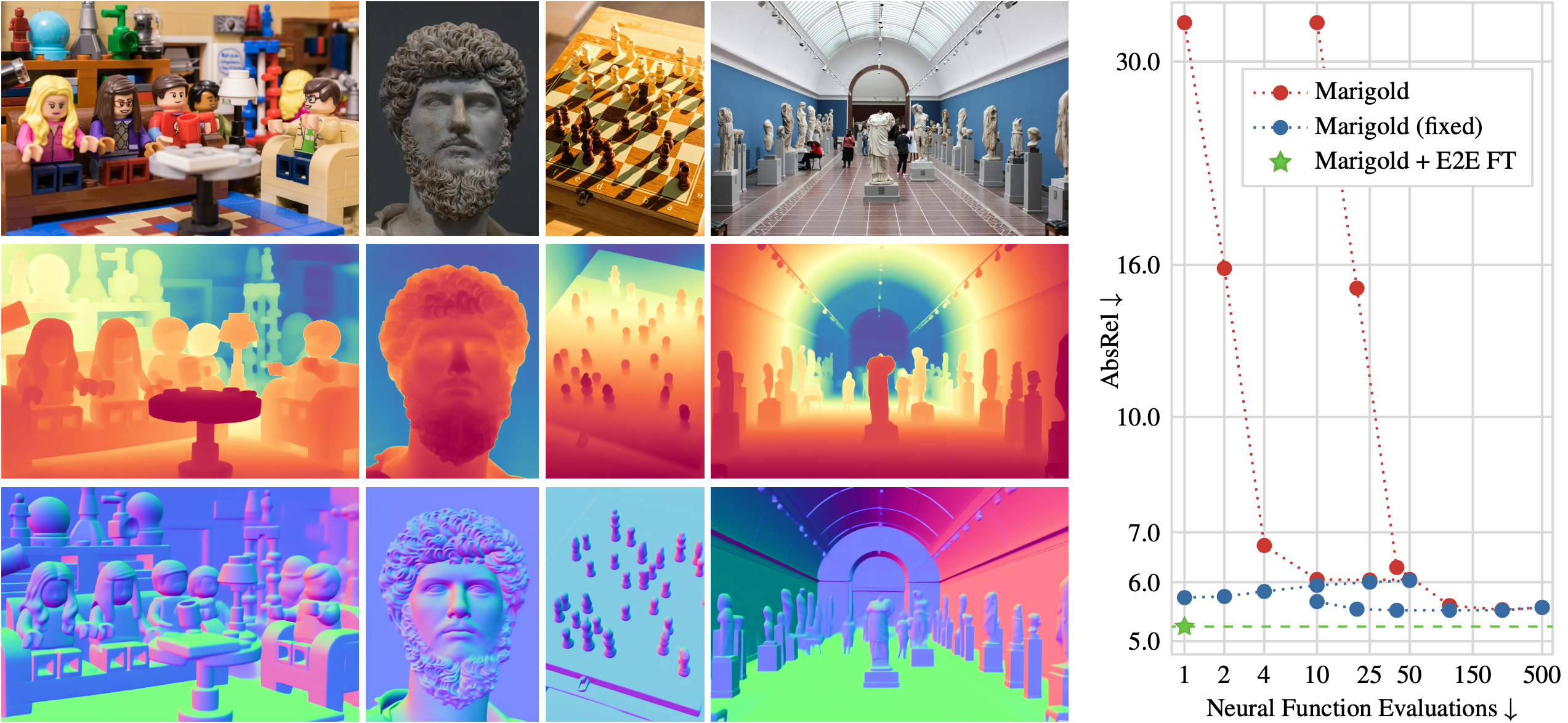
Recent work showed that large diffusion models can be reused as highly precise monocular depth estimators by casting depth estimation as an image-conditional image generation task. While the proposed model achieved state-of-the-art results, high computational demands due to multi-step inference limited its use in many scenarios. In this paper, we show that the perceived inefficiency was caused by a flaw in the inference pipeline that has so far gone unnoticed. The fixed model performs comparably to the best previously reported configuration while being more than 200x faster. To optimize for downstream task performance, we perform end-to-end fine-tuning on top of the single-step model with task-specific losses and get a deterministic model that outperforms all other diffusion-based depth and normal estimation models on common zero-shot benchmarks. We surprisingly find that this fine-tuning protocol also works directly on Stable Diffusion and achieves comparable performance to current state-of-the-art diffusion-based depth and normal estimation models, calling into question some of the conclusions drawn from prior works.
@InProceedings{martingarcia2024diffusione2eft,
title = {Fine-Tuning Image-Conditional Diffusion Models is Easier than You Think},
author = {Martin Garcia, Gonzalo and Knaebel, Karim and Schmidt, Christian and de Geus, Daan and Hermans, Alexander and Leibe, Bastian},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)},
year = {2025}
}
Sa2VA-i: Improving Sa2VA Results with Consistent Training and Inference

Sa2VA is a recent model for language-guided dense grounding in images and video that achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple segmentation benchmarks and that has become widely popular. However, we found that Sa2VA does not perform according to its full potential for referring video object segmentation tasks. We identify inconsistencies between training and inference procedures as the key factor holding it back. To mitigate this issue, we propose an improved version of Sa2VA, Sa2VA-i, that rectifies these issues and improves the results. In fact, Sa2VA-i sets a new state of the art for multiple video benchmarks and achieves improvements of up to +11.6 J&F on MeViS, +1.4 on Ref-YT-VOS, +3.3 on Ref-DAVIS and +4.1 on ReVOS using the same Sa2VA checkpoints. With our fixes, the Sa2VA-i-1B model even performs on par with the original Sa2VA-26B model on the MeViS benchmark. We hope that this work will show the importance of seemingly trivial implementation details and that it will provide valuable insights for the referring video segmentation field.
@article{sa2va2025improved,
title={Sa2VA-i: Improving Sa2VA Results with Consistent Training and Inference},
author={Nekrasov, Alexey and Athar, Ali and de Geus, Daan and Hermans, Alexander and Leibe, Bastian},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2509.19082},
year={2025}
}

